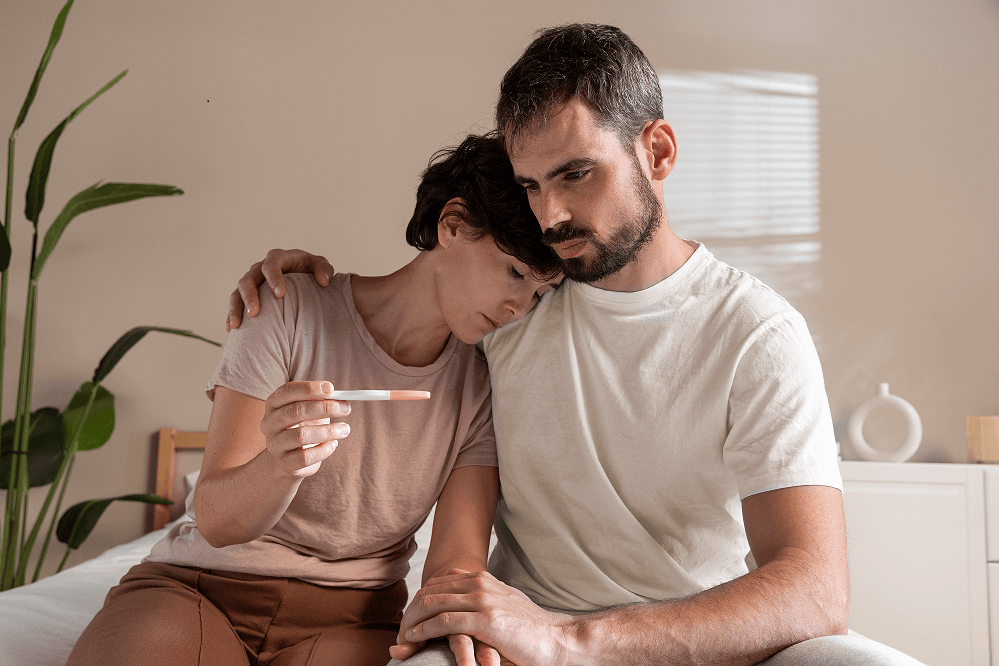
Infertility: Types, Causes, Diagnosis, And Treatment
- Home
- /
- Women's Health & Ayurveda
- /
- Infertility: Types, Causes, Diagnosis,...

Infertility is a condition in which a couple attempting to conceive is unable to create despite a year of regular, unprotected intercourse. Couples who do not meet the criteria for the specified duration can seek medical advice to assess their fertility levels. It can be caused by physical, hormonal, or environmental factors in males, females, or both.
Different circumstances can cause fruitlessness. Therefore, medical care suppliers run a progression of tests to analyse barrenness in couples. An overall actual assessment, evaluation of clinical history, hormonal profiles, ultrasound examinations, etc., structures the determination to assess fruitlessness.
According to Arogya, couples get impacted by infertility, and both men and women experience emotional and psychological distress. Its prevention and care frequently neglect public health concerns, or at least they rank low on the priority list, particularly for low-income countries already experiencing population pressure.
Despite the numerous social, psychological, economic, and physical implications, it is true. However, there has been a rise in awareness of the need to include infertility prevention, care, and treatment in essential medical services.
What Exactly Is Infertility?
Infertility occurs when a male or female is unable to develop due to a problem with either partner’s reproductive system. This can be treated with a primary or secondary source.
If a couple tries but fails to become pregnant within a year, healthcare providers consider them infertile. When a woman is over the age of 35, the time spent trying to conceive reduces to six months for an infertility diagnosis. On the other hand, women over the age of 40 should evaluate right away. Infertility does not include miscarriage or the inability to carry a baby to childbirth.

How Typical Is Infertility?
According to Arogya’s estimation, infertility affects 1 in 10 women between the ages of 15 and 44. In addition, pregnant women who have complications are at risk of losing their child:
- Before week 20 of pregnancy (miscarriage).
- Following week 20 of pregnancy (stillbirth).
Types of Infertility
The evaluation of infertility begins with a general assessment of the patient’s medical history. There are two types of infertility.
- Primary Infertility: This refers to couples who have never previously conceived and are not using any form of contraception.
- Secondary Fertility: This denotes couples who have previously had a successful pregnancy but are unable to conceive on their second try.
Depending on the couple, it can take one of three forms.
- Male infertility: It refers to problems with the male reproductive system.
- Female infertility: This refers to problems with the female reproductive system.
- Unexplained infertility: This occurs when the underlying cause can’t be identified.
Causes of Infertility
There are different reasons for infertility in males and females:
Female Factors Causing Infertility
Female infertility can be caused by several factors. There are numerous reasons why women cannot conceive:
- Damage to Fallopian Tubes: Damage to the fallopian tubes (which transport the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus) can prevent the egg and sperm from making contact. Pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) caused by various infections, endometriosis, or pelvic surgery can cause fallopian tube damage. PIDs are most commonly caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Disturb Ovarian Function/Hormonal Causes: During the menstrual cycle, synchronised hormonal changes occur, leading to the release of an egg from the ovary (ovulation) and the thickening of the endometrium (uterine lining) in preparation for the fertilised egg (embryo) to implant within the uterus.
- Uterine Causes: Infertility may result from abnormal uterine anatomies, such as the presence of polyps and fibroids.
- Cervical Causes: A small percentage of women may have a cervical condition that prevents sperm from passing through the cervical canal due to weird mucus production or a previous cervical surgical procedure.

Male Factors Causing Infertility
Male infertility is caused by low sperm counts, poor sperm quality, or both in more than 90% of cases. On the other hand, male infertility can be caused by a variety of factors, including anatomical issues, hormonal imbalances, and genetic defects. Among the sperm abnormalities are:
- Oligospermia (low sperm counts) /Azoospermia (no sperm): Oligospermia is described as a sperm count of less than 20 million/ml, whereas azoospermia is depicted as the complete absence of sperm cells in the ejaculate.
- Asthenospermia (Poor sperm motility): Asthenospermia occurs when 60% or more of the sperm have abnormal motility (movement is slow and not a straight line) and can lead to infertility.
- Teratospermia (abnormal sperm morphology): For adequate fertility, approximately 60% of the sperm should be normal in size and shape.
However, Sperm abnormalities are caused by a variety of factors such as genetic congenital disabilities, diseases (such as mumps), chemical exposure, and lifestyle habits.

Diagnosis Of Infertility
The doctor determines the type of diagnosis given based on the tests done on both the male and female partners.
This type of test is performed only in cases of male infertility.
- Blood Tests: Testosterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), among other hormones, are measured in the blood.
- Semen Analysis: The first step in specifying the characteristics of semen is frequently a routine semen analysis. Semen volume, total sperm count, and sperm morphology record their characteristics.
- Karyotyping: The karyotyping genetic test looks for potential chromosomal abnormalities that could be passed on to the child.
- Chromosomal Array: This method has a faster turnaround time and fewer problems with no results than karyotyping.
- Ultrasound or Testicular Biopsy: A small piece of testicular tissue is removed via ultrasound or testicular biopsy through a small incision in the scrotum.
Your doctor may ask you to keep track of ovulation symptoms such as basal body temperature and cervical mucus. A home ovulation kit is another option.
The healthcare provider may begin with some basic investigations into female infertility, such as
- Pelvic Exam: Your provider will perform a pelvic exam, which may include a Pap smear, to look for structural problems or disease signs.
- Blood Tests: These are used to measure estrogen, FSH, and LH levels, as well as a progesterone test.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: To determine ovary volume, antral follicle count, uterine anatomy, and any anomalies.
- Hysterosalpingogram: To decide whether the fallopian tubes are blocked or if polyps or fibroids are present.
- Laparoscopy: It is sometimes used to detect damage and blockages in the pelvic structures, ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
- Saline Sonohysterogram(SIS): A saline sonohysterogram (SIS) is a procedure in which your provider fills the uterus with saline (sterile salt water) and performs a transvaginal ultrasound. When the uterus is full, it is easier to see inside.
Treatment Of Male-Female Infertility
Both men and women have access to various infertility treatment options. The type of treatment is personalised based on the diagnosis to ensure the best outcomes. Antioxidants or fertility medications may occasionally be suggested to improve the health of the reproductive system. According to Arogya, others advise surgery for men to treat conditions like varicocele and for females to remove any fallopian tubes or ovarian blockages.

On the other hand, the couple might need more advanced treatment if the tests show more severe infertility. Intrauterine insemination may be involved (where a processed semen sample is inserted into the uterus). In some circumstances, Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in which a single, morphologically normal sperm is chosen to be injected into the oocyte and grown in the lab, and In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF), in which the egg and sperm are cultured and fertilised in the lab, may be advised.
Moreover, some couples may even decide to use donor semen, donor eggs, a gestational carrier, or a surrogate to conceive.
Conclusion
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after a year of trying. Endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and thyroid conditions can all be factors in infertility in women. Low testosterone or low sperm counts may present in men with fertility issues. Age increases your risk of infertility, claims Arogya.
So, to properly diagnose, identify the underlying cause, and treat infertility, a thorough evaluation is required. For routine medical diagnoses or concerns about infertility and the health of the reproductive system, it is best to speak with a healthcare provider about a fertility assessment.
Ayurveda is a natural cure for almost every disease and problem. From hair to foot, you can treat even a little issue with the help of Ayurvedic treatments or herbs. Arogyadham Ayurveda Treatment Centre is an Ayurvedic Treatment Centre in India in where we treat a lot of health and other issues with the use of Ayurvedic medicines. You can also ask our doctors about any query regarding your health issue or anything. We will always be there to help you out. Do not hesitate to contact us anytime.
Finally, if you found this post helpful, feel free to share it on your social media channels to help others benefit. If you need any guidance or support, we are always here to help.
Call: +91-7300783206
Mail: info@arogyadham.in